
Pumpkin is rich in dietary fiber, vitamin A, β-Hushu, its flesh is the same as rice, and is mainly made of sugar and belongs to the entire grain of food. In addition to being a popular decoration for the Christmas Day, there are actually many benefits for pumpkin. What are the nutritional value of pumpkin? Can you eat it every day? The effects and taboos of pumpkin can be understood at once.
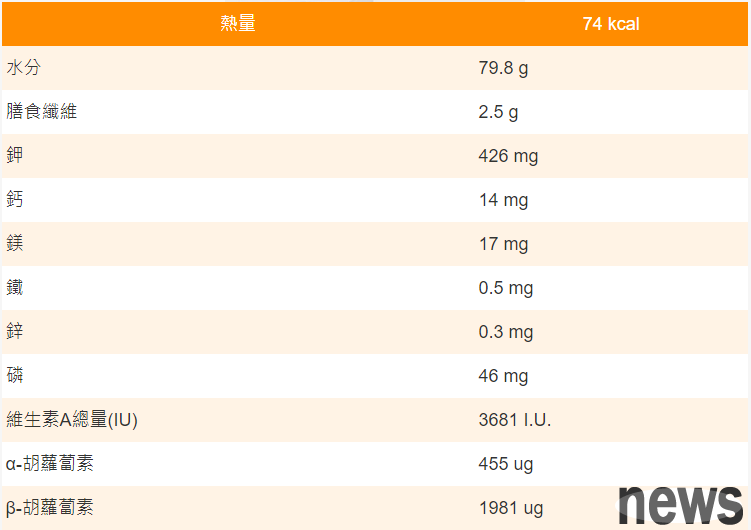
Pumpkin Nutritional IngredientsPumpkin is a family of Cucurbitae, an annual vinegar herb, also known as croaker, gua cucumber, sold melon, and golden gourd. Taiwan produces all year round, with the pumpkin season from March to October. According to the Ministry of Food Nutritional Ingredient Database (new version), the average nutritional ingredients for every 100 grams of pumpkin are as follows:
What are the benefits of pumpkin?
Pumpkin is good, eating more pumpkin is beneficial to human health. The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has also listed pumpkin as one of the 30 anti-cancer fruits and vegetables. According to the Taiwan Cancer Foundation, the β-Hussin, Vitamin C and E contained in pumpkin are antioxidant and can inhibit the growth of cancer cells. Pumpkin has the following 6 benefits:
Eye protection: &beta of pumpkin;-The content of husband is the highest among melons, β-The husband can be converted into vitamin A to protect the eyes and vision. Pumpkin is also a good source of leaf yellow and corn yellow, which helps reduce the risk of senile yellow spot lesions and cataracts, as well as the vitamin C and E contained in pumpkin have antioxidant abilities and can also prevent free radicals from damaging eye cells.
Reduce the risk of chronic diseases and cancer: Too many free radicals can cause chronic inflammation, thereby increasing the risk of chronic diseases. Pumpkin contains antioxidant ingredients such as β-Hussarin, α-Hussarin and β-Hussarin, etc., which help neutralize human free radicals and reduce chronic diseases.
Low heat, helps to reduce fat: Pumpkin has a high dietary fiber content and a low heat content, which can increase foot feeling and promote digestion, help prevent constipation.
Skin protection: Pumpkin contains β-Hussil and vitamin C. β-Hussil has antioxidant ability, can fight skin aging problems, and help relieve inflammation and stabilize the skin. Vitamin C is a nutrient that promotes the production of gelatin and helps maintain skin elasticity.
Protect the cardiovascular: Pumpkin is rich in debris, fiber and vitamin C, which helps maintain cardiovascular health and is rich in antioxidant nutrients. It can protect the aphrodisiac sterol from oxidation, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
Enhance immunity: β-Hussil can be converted into vitamin A, which can strengthen the immune system and resist infection. Pumpkin is rich in vitamin C, which can increase the production of white blood cells and help accelerate the wound to maintain consolidation. It is rich in vitamin E, iron quality, and leaf acid to enhance the immune system.
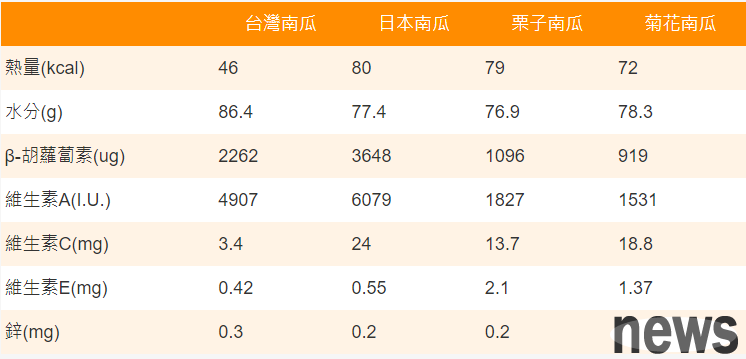
What are the varieties of pumpkins? There are many varieties of 4 varieties of pumpkin, and the nutritional ingredients vary according to different varieties. Nutritionist Gao Minmin once published an article to share the nutritional comparison of four different pumpkins, including Taiwan pumpkin, Japanese pumpkin, chestnut pumpkin and chrysanthemum pumpkin. Among them, Taiwan pumpkin has the lowest heat and the highest moisture content; β-Hushu berry is the highest in Japanese pumpkin; chestnut pumpkin with the highest in vitamin E; and chrysanthemum pumpkin with the highest in hydration content. The following is the nutritional ingredients comparison of 4 types of pumpkins:
What are the taboos for pumpkin?
Pumpkin is rich in nutrients, but a small number of people may experience allergic reactions after eating them. According to the healthline, a foreign health website, pumpkin has a high moisture content and is diuretic. Eating too much pumpkin will increase the body's drainage and salt discharge. If you take diuretics, you should avoid eating them as much as possible.
In addition, pumpkin belongs to the entire grain of rice. Even if the heat is not high, you should pay attention to the amount you consume to avoid taking too much heat, which will lead to obesity.
Pumpkin cuisine DIY: Pumpkin soup, Pumpkin porridge
Pumpkin soup
Ingredients: 1 pumpkin, 1 abalone, 2 garlic cloves, 4 cups of chopped, chicken soup or vegetable soup, 1 cup of fresh butter or plant milk, 2 tons of olive oil or saltless butter, 1/2 teaspoon of cinnamon powder, salt and black pepper (added according to personal taste).
Method:
First cut the pumpkin, remove the seeds and fibers and cut them into small pieces.
After adding olive oil or saltless cream to the soup, add chopped tart and garlic and cook until soft and transparent.
Add the chopped pumpkin pieces to the soup, mix with the avocado and garlic, and stir-fry for about 5 minutes until the pumpkins gradually become soft.
Add chicken soup or vegetable soup and cinnamon powder, salt and black pepper.
Boil the soup and turn it on low heat and cook for about 15 to 20 minutes or until the pumpkin is completely soft.
Once the pumpkin is ripe, use a mixer or mixer to mix the soup to a smooth texture.
Pour the mixed soup back into the soup, add fresh cream or plant milk
and heat it over medium heat. No need to let the soup boil. Add salt and pepper to taste according to your personal taste.
Pumpkin Porridge
Ingredients: 150 grams of pumpkin, 50 grams of pollame or brown rice.
Method:
Peel the pumpkin, seed and cut it into large pieces; wash the porridge with water and clean the rice..
Put the pumpkin and porridge into the pot, add the appropriate amount of water, boil over high heat, and then slowly boil over low heat until the porridge is finished.